Let’s catch up on some of the things that happened in Zephyr land since Zephyr 4.1 was released 3 weeks ago. Over 750 pull requests have already been merged so, like always, I’m of course only covering a very small portion of the tremendous activity of the project.
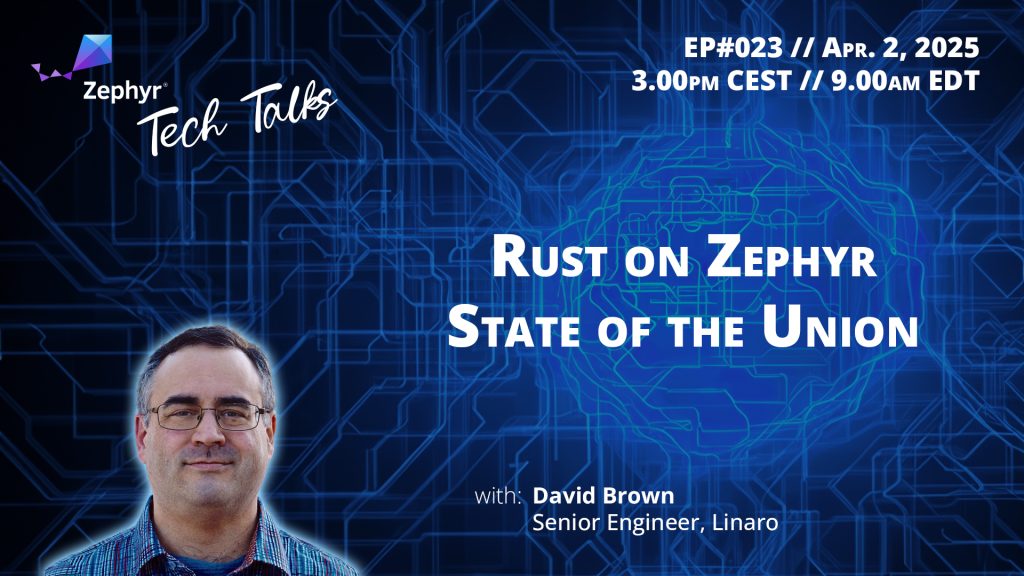
Before diving deeper, don’t forget our upcoming Zephyr Tech Talk next Wednesday, April 2, where David Brown will tell us all there is to know about Rust on Zephyr — what’s there already, what’s coming, and how you can help!
And now for your weekly-ish updates 🙂
Introducing MQTT 5.0 support
We’re getting dangerously close to reaching 90,000 issues/pull requests in the project’s GitHub repository, so it’s not often that an issue in the 20,000 range is being closed 🙂 This week, we just added support for MQTT 5.0 (the project has of course supported MQTT 3.1 for quite a while), which was tracked in issue #21633 open on Jan. 1, 2020!
MQTT 5.0 introduces several improvements over MQTT 3.1(.1), such as the addition of user properties and metadata fields in the CONNECT, PUBLISH, and SUBSCRIBE packets. It also features better error reporting, with reason codes offering clearer feedback when things go wrong.
The addition of MQTT 5.0 support should mostly be transparent for existing MQTT 3.1.1 users 🙂
New boards and SoCs
Some (only a few, really) of the new boards you will probably interested in hearing they are now supported in Zephyr:
- Adafruit ESP32S2 and ESP32S3 Feather boards
- WizNet W5500 EVB Pico2 (PR #84834) and Pimoroni Pico Plus2 (PR #77859) are two new options available to you if you want to play with RP2350-based boards.
- Support for ADC, PWM, I2C, SPI, and TRNG has been added to Arduino UNO R4. (PR #85824)
- … and many new boards and SoCs added by Renesas, STMicroelectronics, Silicon Labs, TI, and others.
Drivers
- Add support for AXP2101 power management IC, which is mostly replacing the AXP192 and is used in several popular devkits from M5Stack and others. (PR #82474)
- New driver for Bosch BMM350, a 16-bit high accuracy/low-noise magnetometer. (PR#85174)
- Vishay VEML6031 Ambient Light Sensor (PR #85818)
- New stepper driver for Allegro A4979 microstepping motor driver (PR #86620)
- TDK ICM45686 IMU sensor (PR #85963)
- PAA3905 optical flow sensor (PR #86644)
Miscellaneous
- The deprecated KSCAN subsystem has now been completely dropped from the codebase, as the Input subsystem has been its replacement for quite a bit now. (PR #87353)
- A new code sample allows you to learn how to interact with stepper motors using the recently introduced Stepper subsystem. (PR #85757)
- The Zephyr Safety Working Group is making great progress gathering requirements, and you can see them at https://zephyrproject-rtos.github.io/reqmgmt/. Feel free to engage with the group through GitHub or via mailing list / Discord if you want to get involved!
A big thank you to the 48 individuals who had their first pull request accepted since Zephyr 4.1 was released, 💙 🙌: @Abd002, @yyounxp, @lfilliot, @leonrinkel, @randyscott, @realhonbo, @mthiede-acn2, @tgcfoss, @skwort, @rdagher, @jangalda-nsc, @MichaelFeistETC, @elmo9999, @ecutm1, @nirav-agrawal, @AndreHeinemans-NXP, @XDjackieXD, @m-braunschweig, @rbudai98, @MJAS1, @DanTGL, @sctanf, @cylin-realtek, @ctourner, @WangHanChi, @dlim04, @verenascst, @Titan-Realtek, @Nitin-Pandey-01, @ckhardin, @Quizzarex, @zafersn, @thorsten-klein, @sgilbert182, @sayooj-aerlync, @tervonenja, @dewitt-garmin, @MyGh64605, @povsel, @sarchey, @etiennedm, @phb98, @petejohanson-adi, @Martdur, @ccpjboss, @JBarberU, @bia-bonobo, and @natto1784.
As always, I very much welcome your thoughts and feedback in the comments below!
If you enjoyed this article, don’t forget to subscribe to this blog to be notified of upcoming publications! And of course, you can also always find me on Twitter and Mastodon.
Catch up on all previous issues of the Zephyr Weekly Update: